What Is a Heat Pipe Solar Collector and How Does It Work?
What Is a Heat Pipe Solar Collector and How Does It Work?
Choosing the right solar collector is confusing. Flat plates may underperform in cold or cloudy climates. Heat pipe solar collectors offer better efficiency and faster heat transfer, making them ideal for modern solar thermal systems.
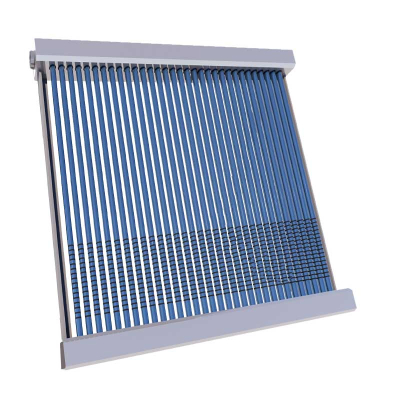
A heat pipe solar collector uses vacuum tubes and a sealed copper pipe to rapidly transfer heat from the sun to a water tank. Inside the heat pipe, a working fluid evaporates when heated, rises to the condenser end, and releases energy through a heat exchanger. This process is highly efficient, works in low-light conditions, and eliminates direct water flow inside the collector, reducing maintenance risks.
Let’s explore how this technology compares to others and why it's a smart choice for solar hot water and thermal heating systems.
How does a heat pipe solar collector work?
A heat pipe solar collector is built using a series of vacuum tubes, each containing a sealed copper heat pipe. Inside the heat pipe is a small amount of fluid that vaporizes at low temperatures. When solar radiation hits the vacuum tube, it heats up the fluid, which then rises to the condenser section located at the top. The heat is then transferred to a circulating fluid—usually water or glycol—through a manifold or heat exchanger. Once the fluid condenses, it flows back down, repeating the cycle continuously.
This closed-loop design avoids direct contact between the system fluid and the solar collector, making it safer, more durable, and less prone to freezing in cold climates.
What is the difference between flat plate and heat pipe solar collectors?
The primary differences between these two types lie in design, efficiency, and climate adaptability:
Efficiency: Heat pipe collectors are more efficient, especially in low temperatures or overcast weather, due to the vacuum insulation and effective heat transfer process.
Durability: Vacuum tubes are better protected against environmental damage compared to the exposed surface of flat plate collectors.
Installation Flexibility: Heat pipe systems work well at steeper angles and in colder environments, making them more versatile for diverse projects.
While flat plate collectors are simple and cost-effective, they struggle in low-sun or freezing conditions. In contrast, heat pipe evacuated tube collectors are ideal for high-demand or professional solar water heating system setups.
Are heat pipe solar collectors better than evacuated tubes?
Actually, these are not mutually exclusive technologies. A heat pipe solar collector uses evacuated tubes as part of its design. The evacuated tube provides thermal insulation, while the heat pipe inside ensures fast and efficient heat transfer.
In systems without heat pipes, the heat is transferred less efficiently or requires direct water flow into the tubes, which can be risky and harder to maintain. So in short: heat pipe + evacuated tube = higher performance and safer system.
What is the disadvantage of heat pipe?
Despite the many advantages, there are a few considerations:
Installation angle: Heat pipe collectors must be installed at a proper tilt (usually 25–70°) to allow gravity-assisted condensation.
Vacuum failure: If a vacuum tube breaks or loses pressure, the efficiency drops significantly.
Cost: They are generally more expensive than basic flat plate systems due to advanced materials and construction.
However, for professional installations and long-term performance, these drawbacks are often outweighed by the benefits.
What are the typical applications of heat pipe evacuated tube collectors?
Heat pipe solar collectors are widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings:
Domestic hot water: Heating water for households using solar thermal energy.
Commercial buildings: Hotels, hospitals, and offices where hot water demand is continuous.
Industrial processes: Pre-heating water or fluids in manufacturing, textile, food, and chemical industries.
Space heating systems: Integrating with radiant floor or fan coil systems for energy-efficient heating.
Solar-assisted heat pump systems: Enhancing hybrid systems for better performance.
Why choose heat pipe technology for your solar thermal collector?
Here are key reasons why many professionals choose heat pipe evacuated tube solar collectors over traditional types:
High efficiency: Excellent performance even in cold climates or partial sunlight.
Modular design: Easy to install, replace, or scale up as project demands grow.
No water inside tubes: Prevents freezing, corrosion, and scaling.
Long service life: Vacuum tubes and copper pipes are durable and low maintenance.
Shengtoku's heat pipe collectors are built with premium-grade borosilicate glass, high thermal conductivity copper pipes, and intelligent manifold designs. They are rigorously tested for wind and snow load, making them ideal for global installations.
How to integrate a heat pipe collector into a solar water heating system?
Integration is straightforward. Heat pipe collectors are typically connected to a pressurized or non-pressurized hot water tank via a closed-loop system with a pump, controller, and heat exchanger.
The system can be configured as:
Passive solar water heater: Using natural circulation (thermosiphon).
Active system: Using pumps and controllers for precise flow and temperature management.
In both cases, the heat pipe ensures fast energy delivery and easy maintenance. Shengtoku offers complete kits and system integration support tailored to your market or climate zone.
Conclusion
Heat pipe solar collectors offer high performance with low maintenance. If you're designing or upgrading a solar water heating system, consider this advanced technology. Contact us to explore custom solutions for your project.